Learn AI Security For FREE With These Amazing Resources
Start your AI security journey today and future-proof your career
AI security is the career of the future.
I have written about this MANY times and keep repeating it on auto-pilot to anyone who wants to future-proof their Cybersecurity career.
But where to start?
A common misconception amongst people is that you need to be super-technical or have a PhD in Data Science to learn AI security
The field is vast enough to accommodate people from both technical and non-technical backgrounds
There is no need to buy expensive courses, as the Internet has some amazing resources you can use.
Here are the ones I would recommend
1 — NIST AI Risk Management Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework has become an industry benchmark companies use to assess their security posture against best practices.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) is poised to do the same for AI Risks.
The NIST AI RMF is a tech-agnostic guidance developed to help companies design, develop, deploy, and use AI technologies responsibly.
NIST frameworks are well-trusted within the industry due to the rigorous validation they undergo from experts all across the globe
This framework is an excellent starting point for people, regardless of their technical background.
It provides a comprehensive approach to managing AI risks through key components such as governance, mapping, measuring, and managing AI systems.
More and more companies will use this framework to manage their AI risks as AI adoption ramps up.
If you find the framework too boring ( which it can be ), then I would recommend using the AI RMF playbook, which is an interactive companion piece to the framework.
It is much more streamlined and engaging than the framework, allowing you to filter those areas that are interested in
2 — AWS GenAI Security Scoping Matrix
I admit I am a bit biased, given that I currently work in AWS
But if you are interested in GenAI security, then the AWS GenAI Security Scoping Matrix is one of the best resources around
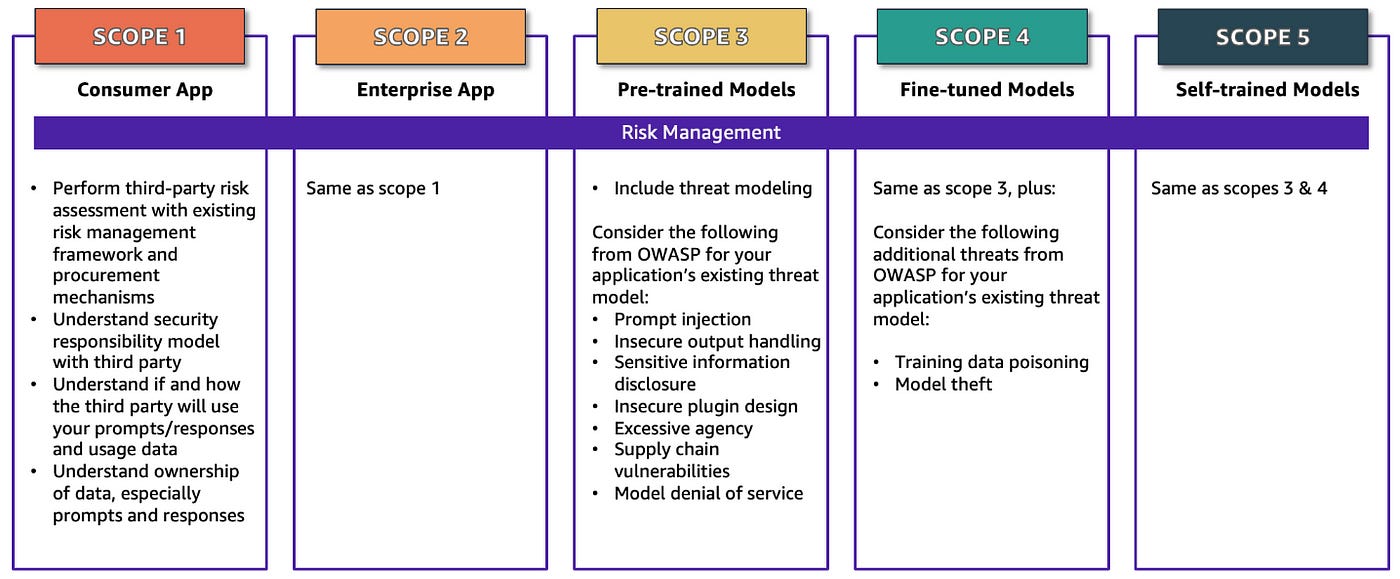
This three-part series helps you understand the different ways of assessing Generative AI risk and how they change depending on the model your company chooses
The concepts are not just restricted to AWS and can be applied to any provider
Highly recommended for those wanting to deep-dive into GenAI risks
3 — OWASP Top 10 For LLM
The OWASP Top 10 is another industry benchmark for web application security.
So it was no surprise when they released their new top 10, this time focusing on Large Language Model Applications
As per OWASP
The OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications project aims to educate developers, designers, architects, managers, and organizations about the potential security risks when deploying and managing Large Language Models (LLMs).
Similar to their previous top 10s, this document lists the most critical vulnerabilities found in LLM applications.
It shows their impacts, how easy it is to exploit, and real-world examples
If you are a CISO or have security leadership responsibilities, it also comes with a great companion piece, the LLM Security & Governance Checklist.
The checklist helps you understand how to assess AI risks and implement an oversight program to mitigate them
4— MITRE ATLAS Framework
The previous frameworks I highlighted are great, but they can be too high-level for someone who likes to dive deep into the technicalities of AI attacks.
This is where ATLAS (Adversarial Threat Landscape for Artificial-Intelligence Systems) comes in.
As per their website
ATLAS is a globally accessible, living knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques against Al-enabled systems based on real-world attack observations and realistic demonstrations from Al red teams and security groups.
As the diagram below shows, ATLAS demonstrates how attackers can compromise AI at each stage and what techniques are used.
An excellent resource if you want to become an AI pent-tester!
Their website also has a great primer on AI security, which you might want to review before you dive into the ATLAS matrix.







